Options and futures are similar trading products that provide investors with the chance to make money and hedge current investments.
An option gives the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to buy (or sell) an asset at a specific price at any time during the life of the contract.
A futures contract gives the buyer the obligation to purchase a specific asset, and the seller to sell and deliver that asset at a specific future date unless the holder’s position is closed prior to expiration.
There is no upfront cost when entering into a futures contract. But the buyer is bound to pay the agreed-upon price for the asset eventually.
The buyer in an options contract has to pay a premium. The payment of this premium grants the options buyer the privilege to not buy the asset on a future date if it becomes less attractive. Should the options contract holder choose not to buy the asset, the premium paid is the amount he stands to lose.
In both cases, you may have to pay certain commissions.
BASICS OF FUTURES AND OPTIONS
feel free to call us +919500077790 info@eqsis.com
Stock Analysis
| M | T | W | T | F | S | S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 |
| 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
| 29 | 30 | |||||
Bullish View
Bearish View
-
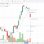 Bearish-GAP-SHORT-BICON-25-10-2019 October 25, 2019
Bearish-GAP-SHORT-BICON-25-10-2019 October 25, 2019
-
 FEDERAL BANK – BEARISH ENGULFING October 17, 2019
FEDERAL BANK – BEARISH ENGULFING October 17, 2019
-
 Cummins India – Bearish Engulfing – 24Sep19 September 25, 2019
Cummins India – Bearish Engulfing – 24Sep19 September 25, 2019
-
 Day29-Tata Motors DVR – Bearish Piercing – 12Sep19 September 12, 2019
Day29-Tata Motors DVR – Bearish Piercing – 12Sep19 September 12, 2019
-
 Day27-Bearish-Engulfing pattern-Tech Mahindtra-09Sep19 September 10, 2019
Day27-Bearish-Engulfing pattern-Tech Mahindtra-09Sep19 September 10, 2019
How this forum help stock traders?
Stock Trading is business, the success depends not just on capital or subscribing advisory services or participating workshops. The factors such as your awareness level about business, Efforts and your contributions, Smartness, Knowledge in analysis and trading instrument, availability of infrastructure and emotional control determine your success.




Hi,
Demand and supply ultimately determine the price of options, several factors have a significant impact on option premiums, which are the spot price, exercise price, volatility, time remaining to expiration, rate of interest and so on…